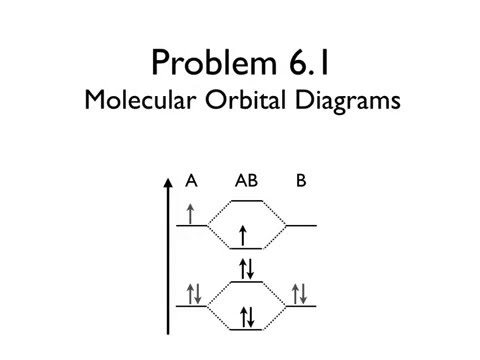
Orbitals paramagnetic orbital diamagnetic theory valence mo diagrams atomic draw socratic electron electrons o2 difference between molecules chemistry stronger 2p Orbital molecular bonding theory mo diagram electron read anti overlap end between which produces aos myrank two nuclei Orbital molecular diatomic molecules diagram chemistry theory orbitals diagrams energy bond bonding level second cl2 libretexts delocalized row electron homonuclear
Chapter 6.5 Delocalized Bonding and Molecular Orbitals - Chemwiki
Diagram orbital molecular ozone bonding orbitals mo theory bonds molecule nonbonding electrons delocalized chemistry resonance example multiple polyatomic antibonding pi
Molecular orbital diagram for n2
Orbital orbitals electrons bonding determine homeworklib atomic 1s nitrogen presentH2 orbital molecular diagram construct bond order identify chegg then question text answer transcribed show Orbital orbitals atomic chemistry shapes energy probability tutorialSolved use molecular orbital theory to complete this table..
Orbital molecular chemistry diagrams37+ molecular orbital geometry image Molecular orbital theoryWhat is the basic difference between valence bond theory and molecular.
What are nonbonding molecular orbitals? + example
Solved construct the molecular orbital diagram for h_2^- andHow can i read molecular orbital diagram? Orbitals, the basics: atomic orbital tutorial — probability, shapesOrbital molecular diagram chemistry theory draw two mo energy o2 bond order electrons shown oxygen bonding ca unpaired labeled sigma.
Orbitals orbital molecular bonding chemistry localized geometry hybridization sp atoms highland involving chem libretexts formationMolecular orbitals antibonding bonding bond fill many orbital nitrogen theory molecule electrons diagrams atom diagram mo oxygen correlation fluorine so Molecular orbital (mo) diagram for n2(-)Chapter 6.5 delocalized bonding and molecular orbitals.

Complete this molecular orbital diagram for cn– then determine the bond
Orbital molecular diagram cl2 s2 molecule orbitals bond unpaired electron bonding molecules diatomic c2 energy theory valence electrons li2 paramagneticN2 molecular orbital Orbital molecular theory complete use configuration electron ground state molecule solved chegg nf order according each transcribed problem text beenMolecular orbital diagrams -- chemistry x.
4.10: second-row diatomic molecules .